
Gas detection sensors: how do they work?
Gas detection sensors are designed to monitor the presence of specific gases in the environment and alert users in case of danger. There are different types of gas detection sensors, each of which uses different technologies to detect the presence of various gases.

Gas detection sensors: technologies
The different technologies used to detect gases vary depending on the application, the environment in which the detector is installed, or even the possible presence of poisoning factors in the air. Sensitron detection systems use four different types of sensors:
Catalytic sensor
Catalytic technology gas detection uses a heated filament that catalyzes the combustion of flammable gases. This process raises the temperature of the filament and changes its electrical resistance, enabling the correct detection of gases such as methane, propane, or hydrogen.
Infrared sensor
Using infrared technology, the absorption of infrared light by gas molecules is measured; in fact, each gas, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) or other specific gases have a characteristic absorption that can be identified.
Electrochemical cell sensor
Electrochemical cell sensors are based on chemical reactions that generate an electric current proportional to the concentration of the target gas and are suitable for the detection of toxic gases such as carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), and oxygen (O₂).
PID sensor
PID technology is used to detect volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other inorganic gases in the air at very low concentrations by using ultraviolet light to ionize gas molecules in the air.
Gas detection sensors: pros and cons
The choice of a gas detection sensor technology depends on several factors; in fact, each sensor has unique characteristics, which have advantages and disadvantages:
Catalytic sensors
- Pros: effective in detecting combustible gases in various concentrations, even at low percentages
- Cons: Susceptible to poisoning by some compounds that may reduce their effectiveness
- Estimated lifetime: about 5 years
Infrared sensors
 Pros: do not degrade over time due to exposure to target gases, offer long life and stability
Pros: do not degrade over time due to exposure to target gases, offer long life and stability- Cons: More expensive, require accurate calibration for different gases
- Estimated lifetime: more than 5 years

Electrochemical cell sensors
- Pros: high specificity for toxic gases, allow very accurate detection
- Cons: Durability typically between 1 and 2 years, can be affected by changes in temperature and humidity
- Estimated lifetime: about 3 years

PID sensors
- Pros: highly sensitive, capable of detecting ppb gas concentrations
- Cons: Non-specific, detect a wide range of VOCs without distinguishing between them
- Estimated lifetime: about 2 years
Discover our products
Our gas detection systems offer a safe and effective solution, ensuring accurate and timely measurements. Discover the product best suited to your needs:
SMART 3G D2
Suitable for detecting flammable substances, toxic gases, refrigerants and oxygen in classified areas. Certified ATEX, IECEx and SIL2/3
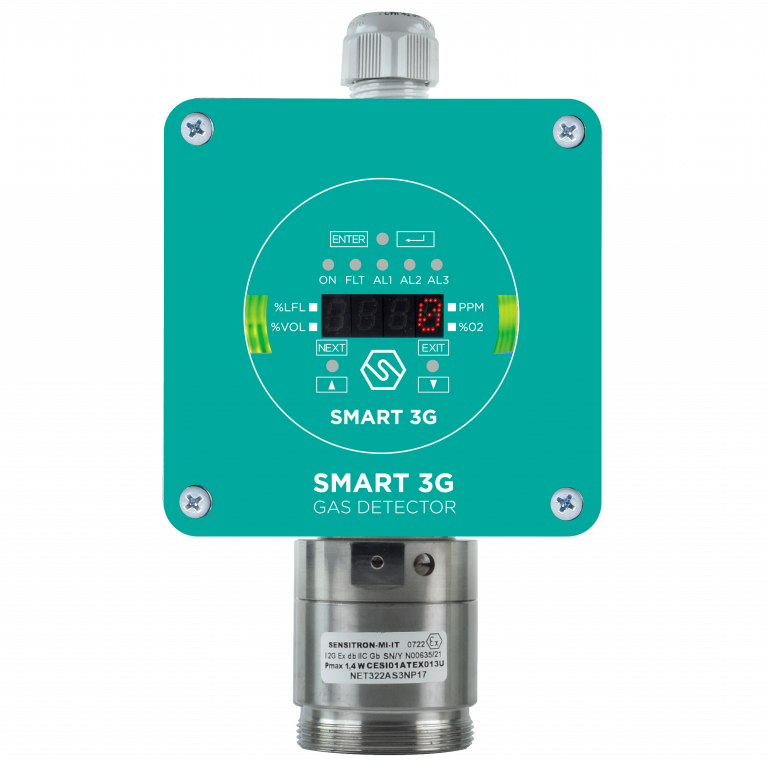

SMART 3G D3
Suitable for detecting in classified areas, Certified ATEX, IECEx and SIL2/3, allows non-intrusive field calibration.
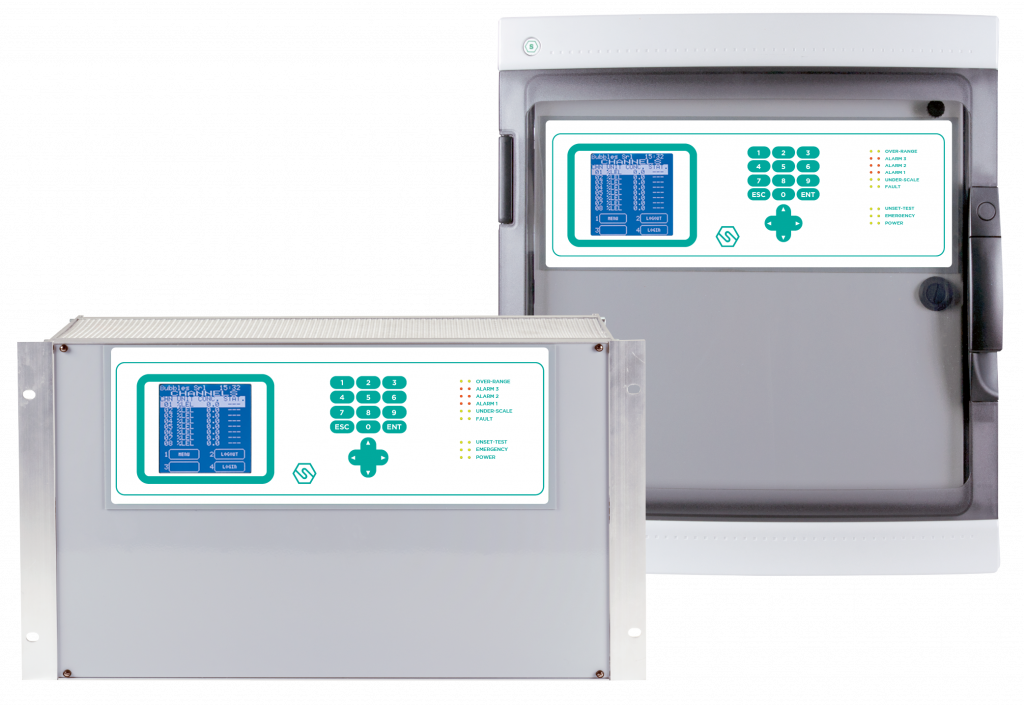

MULTISCAN ++S1/++S2
Designed to meet the widest demand from the market, they allow management of up to 264 detectors. ATEX and SIL certified.


