
Paper industry and gas detection

Paper industry: what are the most common gases
Some of the most important and common gases to monitor in the paper industry are:
- Chlorine (Cl₂): Used to bleach paper, it is extremely toxic and can cause serious health damage. Detection is crucial especially in storage and chemical processing areas.
Sulfur dioxide (SO₂): Released during some combustion and chemical treatment processes, it is irritating to the eyes and respiratory tract. - Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S): Produced in the decomposition of organic material in anaerobic environments, it can be lethal in high concentrations.
- Methane (CH₄): Can accumulate in waste treatment areas or landfills associated with the disposal of waste from the production process.
- Solvent vapors: Often used in some chemical treatments or in the production of coated paper, these vapors can be flammable and require constant monitoring.
- Oxygen (O₂): It is important to monitor both excess and deficient oxygen, as levels that are too low can create an atmosphere hazardous to breathing, while levels that are too high can increase the risk of fire in the presence of combustible materials.


Technologies for gas detection in the paper industry
Within the paper industry, stationary gas detection systems constantly monitor the environment and report any leaks or hazardous gas concentrations in real time. The main technologies used are:
- Infrared sensors: Used to detect flammable gases. Infrared sensors are particularly suitable for environments with high gas concentrations.
- Electrochemical sensors: Used mainly to detect toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide, they are accurate and very sensitive sensors.
- Catalytic sensors: By burning a small amount of gas on a catalyst, they convert the temperature rise into an electrical signal proportional to the gas concentration.
Paper industry: where gas detection is important
In the paper industry, various production processes involve the use or generation of potentially hazardous gases, including:
- Pulping: A process in which fibers are prepared, in which wood or other fibrous materials are converted into a pulp of cellulose fibers for papermaking. This process can be mechanical, chemical, or a combination of both.
- Bleaching: A bleaching process in which the natural color of the pulp is removed to produce a lighter paper product; this process often employs harsh chemicals.
- Recycled paper production: In the process of recycling paper, the material is broken down into fibers for later reprocessing. This process can generate gases due to the degradation of used paper and chemical treatment.

Our products for gas detection in the paper industry
For gas detection within the paper industry, the SMART 3G and SMART S series of gas detectors are ideal:
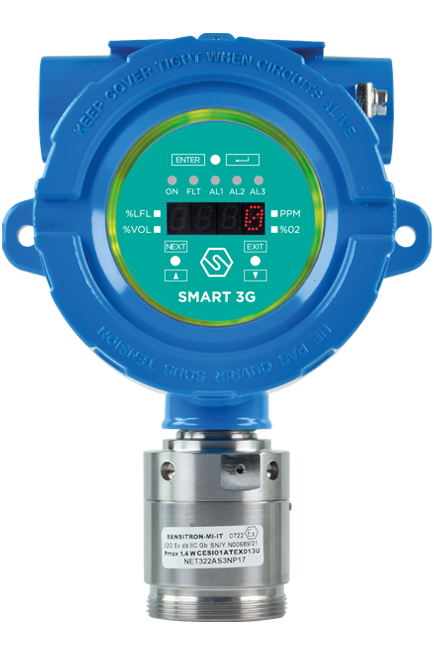
SMART 3G D2
Suitable for detecting flammable substances, toxic gases, refrigerants and oxygen in classified areas.
Certified ATEX Category 2 for Zone 1, IECEx and SIL2/3
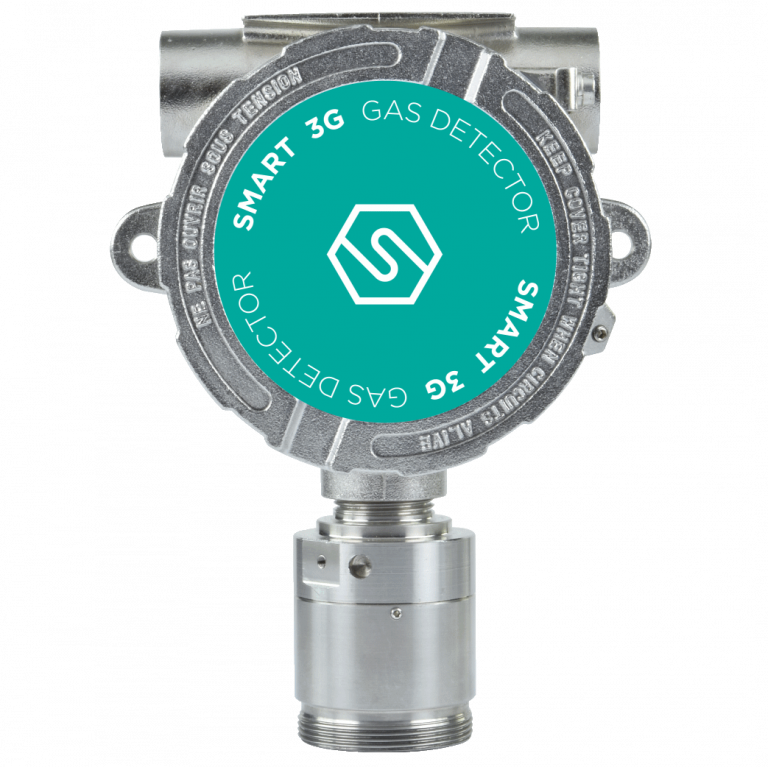

SMART 3G Gr.1
ATEX Group 1 certified, ideal for detecting flammable substances and toxic gases in mines, tunnels or areas classified Group 1.
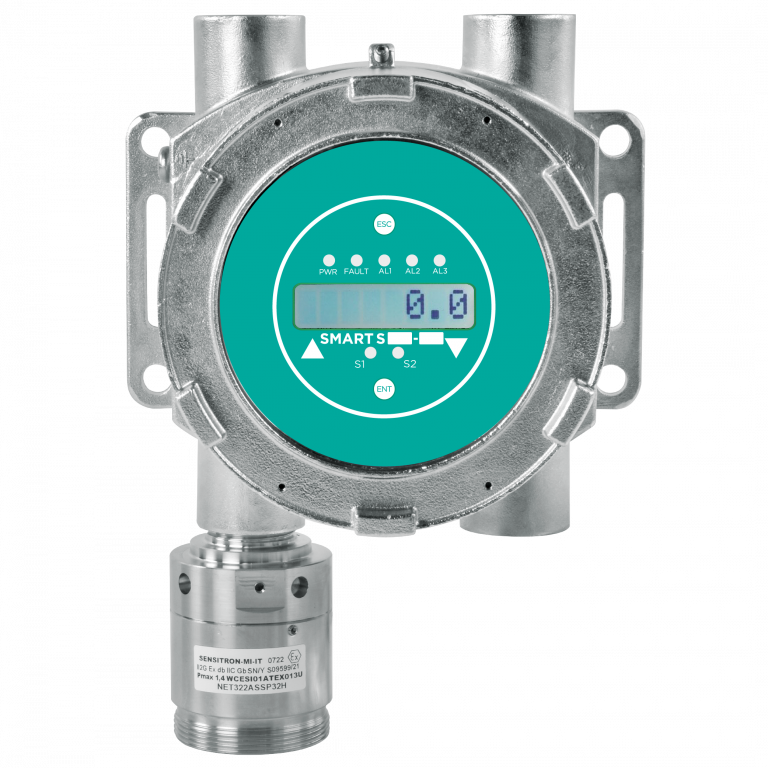

SMART S SS
ATEX certified for Zone 1, SIL2 Hardware and SIL3 Software, optional Hart Modem and with stainless steel housing.
Explore our spaces in virtual reality
Within the Sensitron metaverse you can explore application realities reconstructed in virtual reality. Find out more about who we are and what we do, walk inside a production area and learn more about the dangers of gas.


