
Steel industry and gas detection
In the steel industry, gas detection is critical to ensure worker safety and prevent accidents. This industry is characterized by the production and handling of high quantities of materials and substances that, if not properly monitored, can pose serious risks.

Steel industry: what are the most common gases
Some of the most dangerous and common gases in the steel industry are:
- Carbon monoxide (CO): This is a colorless, odorless gas produced during combustion processes and in the iron and steel processing stages. It is highly toxic and can cause poisoning if inhaled in large quantities.
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂): This is a common by-product of combustion and heat production processes, and although it is not toxic at low concentrations, it can cause suffocation in enclosed or poorly ventilated environments.
- Sulfur dioxide (SO₂): It is emitted during combustion of sulfur-containing fuels. It is irritating to the respiratory tract and can cause severe respiratory problems.
- Oxygen (O₂): It is also essential to monitor the concentration of oxygen in the air, as too low levels can cause asphyxiation, while too high levels can increase the risk of fire and explosion.
- Flammable gases (methane, hydrogen, etc.): During some stages of processing, flammable gases can accumulate which, if undetected, can cause explosions.


Technologies for gas detection in the steel industry
Installed at critical points in steel plants, stationary gas detection systems constantly monitor the environment and report any leaks or dangerous gas concentrations in real time. The main technologies used are:
- Infrared and catalytic sensors: Used to detect flammable gases. Infrared sensors are particularly suitable for environments with high gas concentrations, while catalytic sensors are useful for more specific measurements of various flammable gases.
- Electrochemical sensors: Used mainly to detect toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide, they are accurate and very sensitive sensors.
Steel industry: certifications for gas detection systems
Certifications for gas detection systems in the steel industry are critical to ensure that the devices comply with safety regulations and the performance required in hazardous environments. Below are some of the main certifications that gas detection systems must obtain to be used in industrial environments such as the steel industry:
- ATEX: European Directive 2014/34/EU, covers equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres.
- IECEx: International Standard IEC 60079, is uan international certification for equipment used in explosive atmospheres.Similar to ATEX certification, but at the international level, it verifies that equipment is suitable for use in hazardous environments on a global scale.
- ISO 9001: International standard for quality management systems, certifies that the manufacturing company follows rigorous processes to ensure quality, reliability and safety of its products, including gas detection systems.
Our products for gas detection in the steel industry
For gas detection within the steel industry, the SMART 3G gas detector and the SMART S gas detector series are ideal:
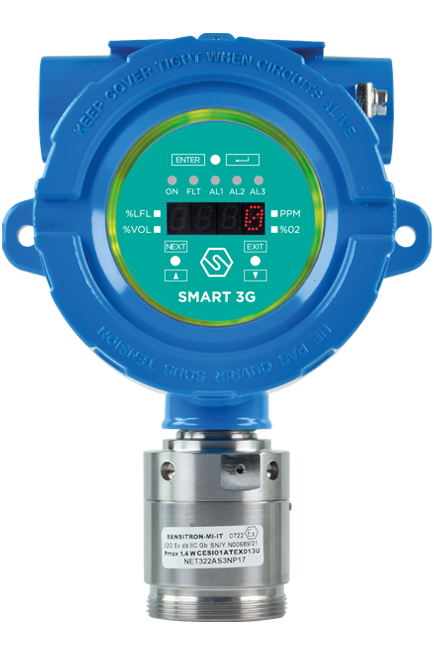
SMART 3G D2
Suitable for detecting flammable substances, toxic gases, refrigerants and oxygen in classified areas.
Certified ATEX Category 2 for Zone 1, IECEx and SIL2/3
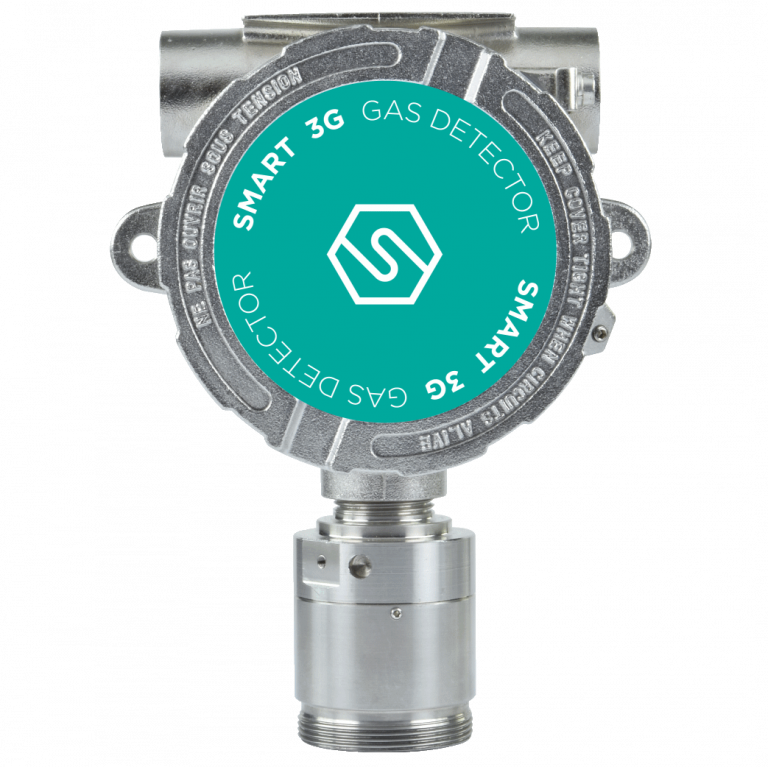

SMART 3G Gr.1
ATEX Group 1 certified, ideal for detecting flammable substances and toxic gases in mines, tunnels or areas classified Group 1.
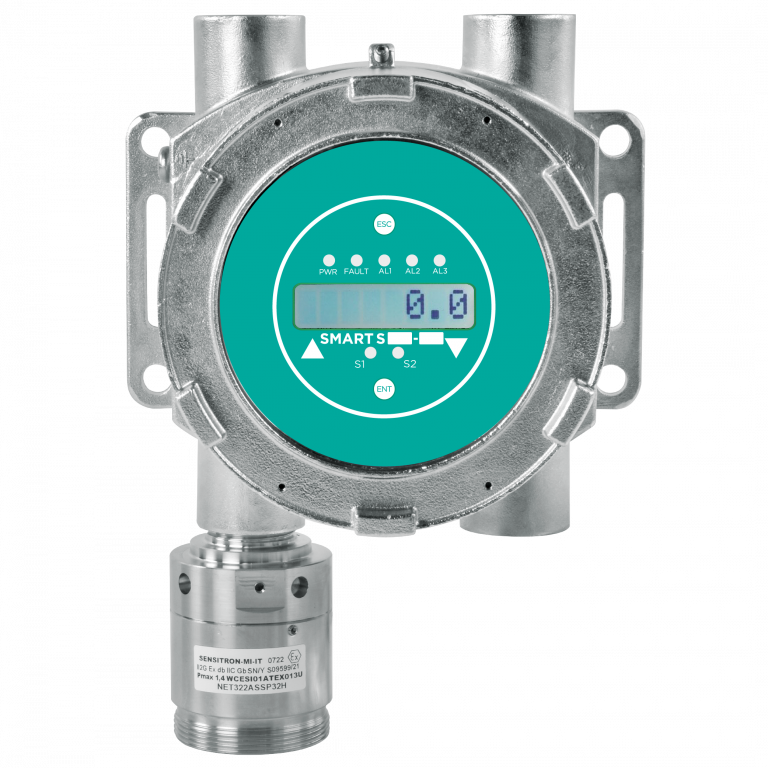

SMART S SS
ATEX certified for Zone 1, SIL2 Hardware and SIL3 Software, optional Hart Modem and with stainless steel housing.


