
VOCs and gas detection in industries
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) represent a wide range of chemicals that readily evaporate into the air at room temperature. These compounds, found in many industrial processes, can have a significant impact on both human health and the environment. Detection and monitoring of VOCs in industries are therefore critical to ensure worker safety and minimize environmental pollution.

VOCs: why it is important to detect them

In industries, VOCs are emitted during many production processes, including solvent use, chemical production, painting and surface treatment. Exposure to high levels of VOCs can cause a range of health problems:
- Eye, nose and throat irritation
- Central nervous system disorders
- Chronic respiratory diseases
In addition, VOCs contribute to the formation of tropospheric ozone, an air pollutant that can have harmful effects on both the environment and human health.
VOC: common uses

Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) find use in a wide range of industrial and domestic sectors due to their unique chemical and physical properties:
- Solvents for paints and coatings: One of the most common uses of VOCs is as solvents in paints, coatings and enamels. These compounds facilitate the application of paints and coatings by improving flow and drying time. Once applied, VOCs evaporate quickly, allowing the paint to cure and form a protective film on the surface
- Chemical Industry: VOCs are widely used as chemical intermediates in the production of a wide range of industrial chemicals. For example, ethylene and propylene, two important VOCs, are used in the production of polymers and plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene
- Cleaning products: Many detergents and cleaning products contain VOCs as active components. These compounds help dissolve grease, dirt and stains on different surfaces, improving the effectiveness of products. Some common examples include ethanol and isopropanol, which are used in disinfectants and all-purpose cleaners
- Pharmaceutical Industry: In the pharmaceutical industry, VOCs are used as solvents in the production of drugs and for the synthesis of active ingredients. For example, methanol and acetone are used in various pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to extract and purify active ingredients
- Cosmetics industry: Many perfumes and cosmetics contain VOCs to improve fragrance and product stability. Some volatile VOCs are used to ensure that fragrances evaporate gradually, leaving a lingering fragrance on the skin. Aromatic alcohols, such as benzylalcohol, are common examples of VOCs used in perfumes
VOCs: characteristics
The main characteristic of VOCs is their volatility, that is, their ability to evaporate easily at room temperature. This property arises from their low vapor pressure, which allows the molecules to move rapidly from the liquid to the gas phase, diffusing into the air. They are composed of organic molecules, which contain carbon and hydrogen, often combined with other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, chlorine or sulfur. This diversity in chemical composition results in a wide range of VOCs, each with different chemical and physical properties. Many VOCs are chemically reactive and can interact with other compounds in the atmosphere, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), to form tropospheric ozone, a harmful air pollutant. Some VOCs, such as aromatic compounds (e.g., benzene), are particularly reactive and can contribute significantly to air pollution.
Technologies used to detect VOCs
A PID technology sensor can be used for the correct detection of VOCs. These are extremely sensitive instruments and can detect VOCs at very low concentrations. Its lifetime depends on various factors, including the quality of the sensor itself, operating conditions and frequency of use. However, key elements, such as the UV lamp, have life cycles ranging from 6 to 12 months, necessitating maintenance for replacement. In addition, depending on the manufacturer’s instructions, periodic calibration of the detector will also be necessary to ensure accurate detection.


Discover our products in Virtual Reality
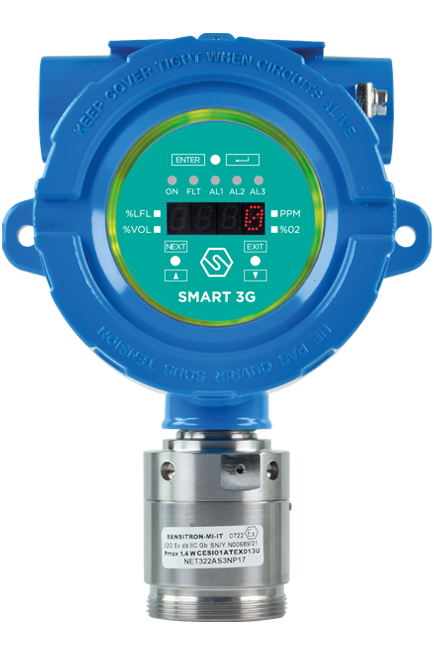
SMART 3G D2
Suitable for detecting flammable substances, toxic gases, refrigerants and oxygen in classified areas.
Certified ATEX, IECEx and SIL2/3
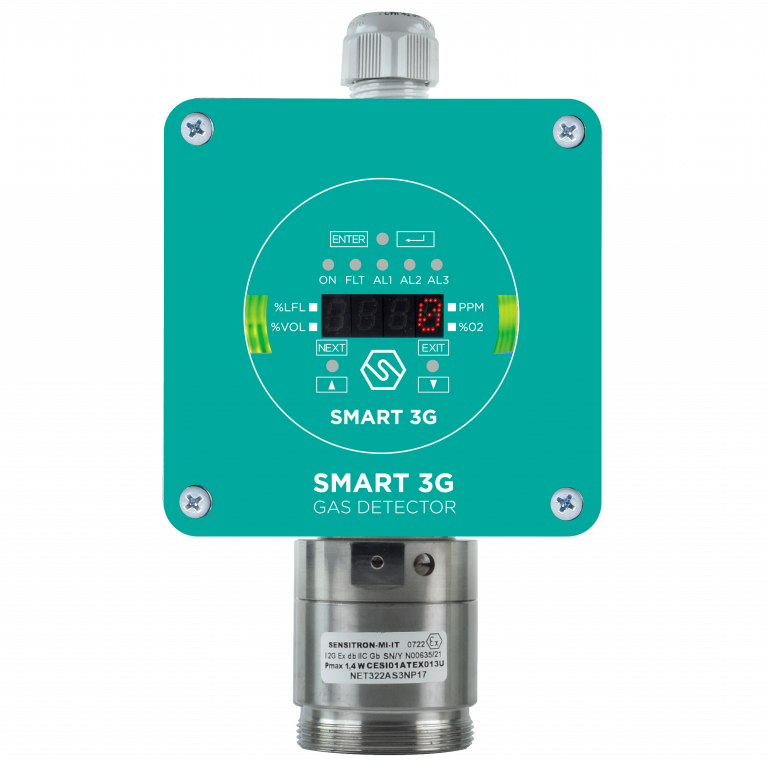

SMART 3G D3
Suitable for detecting in classified areas, Certified ATEX, IECEx and SIL2/3, allows non-intrusive field calibration.

SMART 3G C2-LD
SMART 3G-C2-LD gas detectors are used to detect, in classified areas, the presence of flammable substances (% LFL), toxic gases in ppm, refrigerant gases or for the detection of oxygen deficiency or excess.


